Work with workitem flows
To access worktypes when you create a workitem flow:
- Workitems > Worktype> View permission
To create and modify worktype rules:
- Workitems > Flowruleoncreate > Add permission
- Workitems > Flowruleoncreate > View permission
- Workitems > Flowruleoncreate > Edit permission
- Workitems > Flowruleoncreate > Delete permission
- Workitems > Flowruleonattributechange > Add permission
- Workitems > Flowruleonattributechange > View permission
- Workitems > Flowruleonattributechange > Edit permission
- Workitems > Flowruleonattributechange > Delete permission
- The maximum length of a flow name is 200 characters and it cannot contain a slash
/or end in-debug. - You cannot duplicate names for workitem flows.
Use a dedicated workitem flow in Architect to manage workitems without depending on data actions. You can use a workitem flow, for example, to adjust the assignee, due date, expiry date, priority, or status of a workitem. You can also disconnect, terminate, or transfer a workitem with a workitem flow.
Workitem flows enable you to perform such tasks as:
- Invite various stakeholders to work collaboratively in Architect to define the business logic for the desired work automation.
- Process workitems during their entire life cycle.
- Read and update built-in and custom workitem attributes.
- Reassign the workitem by transferring it to a different queue or agent.
- Retract the workitem from the assigned agent.
- Configure the workitem flow to execute automatically on workitem creation and status change without the need to set up a trigger.
Use case examples
- Automate repetitive tasks such as data validation or requests for missing information.
Example 1: Preprocess bookings in a contact center.
Benefits: enhanced efficiency, reduced response time, and greater data accuracy.
Work automation tasks:
- Validate the customer data: when the customer submits a booking, work automation can launch a pre-configured workitem flow that starts by validating the received customer data. For example, the workitem flow can check if mandatory data fields are complete and in the correct format. The workitem flow can also cross-reference the customer data with CRM databases to ensure accuracy.
- Identify missing information: Work automation recognizes missing or incorrect data and fetches the missing information from business systems, for example, a CRM system.
- Update the booking workitem: when the customer provides the missing data, work automation can update their booking with the new information.
- Automate task assignment.
Example 2: Preprocess insurance claims for task assignment.
Benefits: faster resolution, greater operational efficiency.
Work automation tasks:- Determine the insurance category for proper routing: when a customer makes an insurance claim, work automation can launch a pre-configured workitem flow that starts by checking the customer profile and determines the insurance category (automobile, home, life, and so on).
- Assign the work automation task to the appropriate queue on task status change: When the workitem’s status changes to ‘Waiting to assign’, based on the determined insurance category, work automation can assign the workitem to the appropriate queue.
- Collect data for claim handling: When the workitem’s status changes to ‘Assigned’, work automation can automatically collect the custom attributes of the associated worktype. For example, the insurance limit of the customer, or any previous claim history.
Create a workitem flow
Keep the following key points in mind:
- Every workitem flow is based on and associated with a specific worktype. A workitem flow can only be associated with a single worktype.
- A worktype can only be associated with a single workitem flow. In other words, you can only create one workitem flow per worktype.
- If you want to create another workitem flow for a worktype, you must delete the existing workitem flow that is associated with that worktype.
- After a workitem flow is created, you cannot change which worktype the workitem flow is associated with.
- Set up the worktype before you create the workitem flow. You can only create a workitem flow with a worktype.
- The worktype, its statuses, and its collection of custom attributes (schema) are all dependencies of the workitem flow. In other words, flow authors can reference them within the workitem flow.
- Architect notifies flow authors about worktype schema changes or if the worktype no longer has a custom schema associated with it.
- If the associated worktype is deleted after a workitem flow is created or generated, Architect displays a validation error that indicates that the associated worktype is no longer valid. You cannot publish your workitem flow because you cannot change the associated worktype after you create a workitem flow.
- Search for flows by worktype in the Dependency Search tab in the Architect home page.
- Find the associated worktype in the Dependencies pane under Resources and in Workitem Flow Settings.
- To set rule conditions for workitem flow execution when a workitem is created or its status changes, navigate to the Rules tab of the associated worktype under Admin > Task Management Menu > Orchestration > Work Automation > Worktypes. For more information, see Define a worktype (add new rules tab).
Complete the following configuration steps before you create your workitem flow:
- (Optional) Create custom attributes.
- Create a workbin.
- Create a worktype.
To create a workitem flow, follow these steps:
- From the Architect home page, click or hover over the Flows menu and select Workitem flow.
- Click Add. The Create Workitem Flow dialog box opens.
- In the Name field, enter a unique name for the flow.
- (Optional) In the Description field, add a short sentence or phrase to describe this flow.
- Click the Worktype list and select the worktype based on which you want Architect to generate the workitem flow.
Notes:- Architect displays the worktypes that have been created under Admin > Task Management Menu > Orchestration > Work Automation > Worktypes.
- You can only create one workitem flow per worktype.
- You cannot select a worktype that is already in use by another workitem flow.
- Click the Default Language list and select the flow's default supported language.
- Click the Divisions list and select the division in which to place the flow.
- Use the Generate Flow Logic toggle to auto-generate the default flow logic for event handling and statuses based on their configuration in the selected worktype.
- Click Create Flow. The flow's configuration page opens.
worktypeName or worktypeId to set the worktype on the workitem flow. For more information, see Define Architect flows using YAML.Design logic behind workitem flows
Architect automatically generates your initial workitem flow based on the worktype that you select. When the rule condition in the worktype configuration is set to Creation, the respective Event Type in the workitem flow is set to workitemCreated. Similarly, when the rule condition is Status Transition or Dates, Architect sets the Event Type in the workitem flow to workitemStatusChange or workitemDateBasedEvent respectively.
Architect applies the following design logic depending on the worktype configuration:
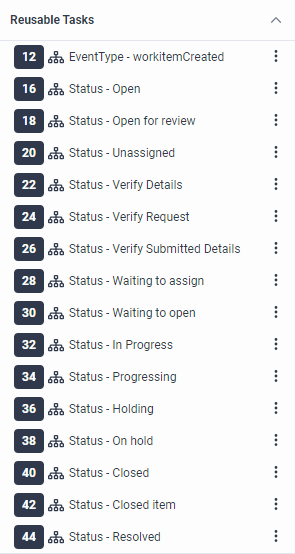
- Architect generates a Reusable Task for the
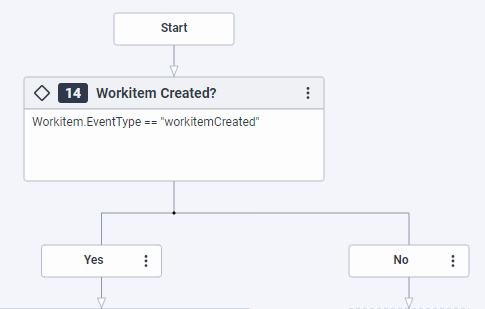
workitemCreatedevent type and all the worktype statuses that have been configured in the associated worktype. Flow authors can configure the required business logic for handling workitems when they are created and the various workitem status changes in the respective Reusable Tasks. - A workitem can launch a workitem flow or it can be sent to a queue for assignment at creation time. Architect adds a Decision action below Start in the Initial state to determine whether the
workitemCreatedevent type triggered the execution of the workitem flow. - If the flow was launched on workitem creation, Architect calls the EventType – workitemCreated Reusable Task with a Call Task action to execute the business logic that the flow author specified for handling workitems on creation.
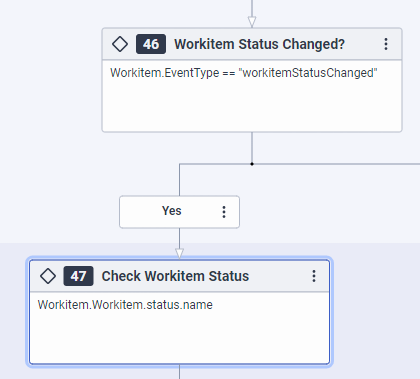
- If the flow was not launched because of a
workitemCreatedevent, Architect checks whether the flow was triggered by aworkitemStatusChangedevent with another Decision action.
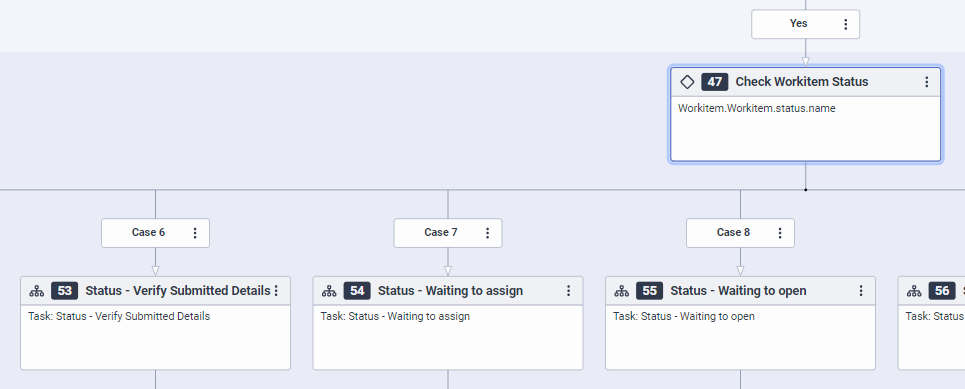
- If the flow is running because of a status change, Architect checks what the name of the new status is. Then, it calls the corresponding Reusable Task with a Switch action to execute the configured business logic for handling the specific status update.
- If the flow was not launched because of a
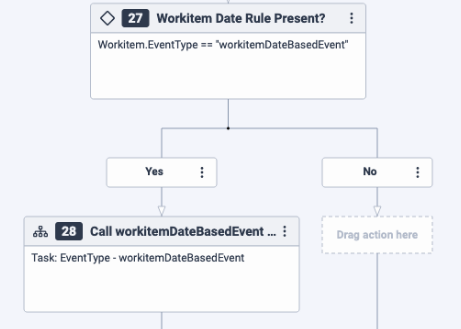
workitemCreatedevent or aworkitemStatusChangedevent, Architect checks whether the flow was triggered by aworkitemDateBasedEventwith another Decision action. - If the flow is running because of a
workitemDateBasedEvent, Architect checks the name of the date rule. Then, it calls the corresponding Reusable Task with a Switch action to execute the configured business logic for handling the workitem based on the date rule. The date rules allow you to set conditions based on the due date, expiration date, or life span of a workitem. When these conditions are met, the workitem triggers the associated workitem flow instance. - Architect adds an Exit Workitem Flow action at the end of the workitem flow.
Customize your workitem flow
You can customize the generated workitem flow in the following ways:
- You can add custom business logic to handle workitems during the event types such as workitem creation, status change, or date-based event.
- You can use the following workitem-related Architect actions to handle workitem updates:
- You can use built-in and custom variables to reference, update, make decisions, or take other actions based on various aspects of your workitem:
- For example, you can use the
Workitem.Workitem.customFieldsvariable to reference items that have been defined as part of the custom schema associated with the worktype.Imagine the following scenario. You want to check what tier of a customer or loyalty program a customer belongs to and update the workitem’s custom label or priority accordingly. You can use, for example, a Switch action to check the tier level, and define Boolean expressions in the Case configuration boxes for each tier level viaWorkitem.Workitem.customFields.<attribute for the tier levels in your custom schemain each expression (Workitem.Workitem.customFields.customer_level_enum == "gold"). Then, you can add an Update Workitem action for each Case that updates the custom label field or add a Set Priority action to update the priority of the workitem.
Click the images to enlarge.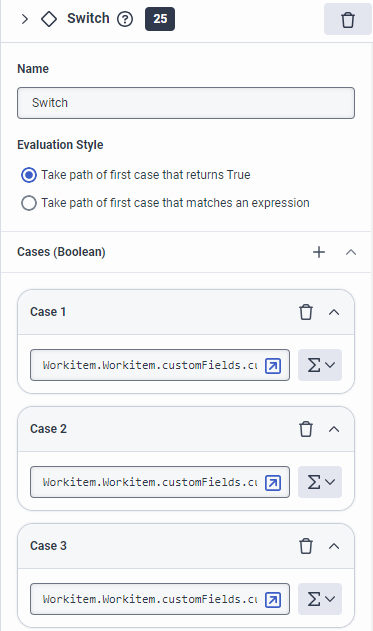
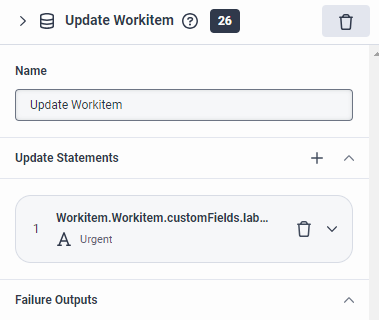
- For example, you can use the
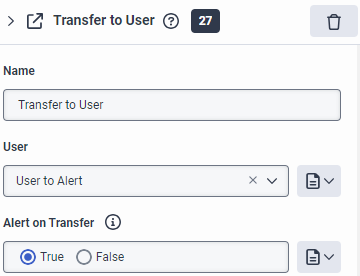
- You can add alerts for transferring a workitem to a user with a Transfer to User action.
- You can use workitem-related functions (
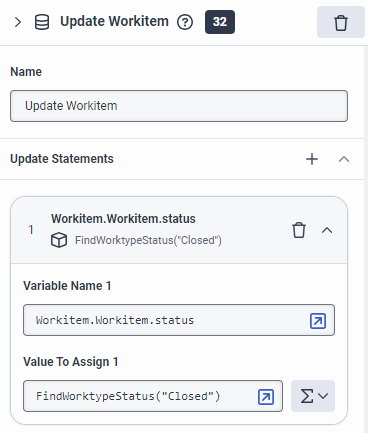
FindWorktypeStatus, FindWorktypeStatusById) to update the status of a workitem in an Update Workitem action.
Limitations
- Execution limits:
- There can be a maximum of one workitem flow execution at a time per workitem. If a rule condition is met for a workitem and there is a workitem flow already running for that workitem, Architect will not launch the workitem flow.
- Disconnect Workitem: There is a limit on the maximum number of Disconnect Workitem action executions per workitem flow instance (
action.disconnectworkitem.invocations.per.flow.max). For more information, see Limits in the Genesys Cloud Developer Center. - Terminate Workitem: There is a limit on the maximum number of Terminate Workitem action executions per workitem flow instance (
action.terminateworkitem.invocations.per.flow.max). For more information, see Limits in the Genesys Cloud Developer Center. - Update Workitem: There is a limit on the maximum number of Update Workitem action executions per workitem flow instance (
action.updateworkitemdata.invocations.per.flow.max). For more information, see Limits in the Genesys Cloud Developer Center. - Set External Tag: There is a limit on the maximum number of Set External Tag action executions per workitem flow instance (
action.setexternaltag.invocations.per.flow.max). For more information, see Limits in the Genesys Cloud Developer Center. -
Set Priority: There is a limit on the maximum number of Set Priority action executions per workitem flow instance (
action.setpriority.invocations.per.flow.max). For more information, see Limits in the Genesys Cloud Developer Center. - Set Skills: There is a limit on the maximum number of Set Skills action executions per workitem flow instance (
action.setskills.invocations.per.flow.max). For more information, see Limits in the Genesys Cloud Developer Center. - Transfer to ACD: There is a limit on the maximum number of Transfer to ACD action executions per workitem flow instance (
action.transfertoacd.invocations.per.flow.max). For more information, see Limits in the Genesys Cloud Developer Center. - Transfer to User: There is a limit on the maximum number of Transfer to ACD action executions per workitem flow instance (
action.transfertouser.invocations.per.flow.max). For more information, see Limits in the Genesys Cloud Developer Center.
- Flow launch limit: There is a limit on the number of times an individual workitem can launch a workitem flow per day (
workitem.workitemflow.launch.per.day). For more information, see Limits in the Genesys Cloud Developer Center. - Flow launch rate limit: There is a limit on the maximum number of launches for a specific workitem flow per minute (workitem.flow.launch.rate.per.minute). For more information, see Limits in the Genesys Cloud Developer Center.
- Flow runtime limit: There is a limit on the maximum number of seconds a workitem flow can execute for before the workitem flow invokes error handling (
flow.type.workitem.duration.seconds.max). For more information, see Limits in the Genesys Cloud Developer Center. - Flow size limit: There is a limit on the maximum size in bytes allowed for a workitem flow (
flow.type.workitem.size.bytes.max). For more information, see Limits in the Genesys Cloud Developer Center. - Flow action limit: There is a limit on the maximum number of actions a workitem flow can execute before the flow invokes error handling (
flow.type.workitem.action.executions.max). For more information, see Limits in the Genesys Cloud Developer Center.
Built-in variables
| Name | Type | Collection? | Read Only? | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow.IsTest | Boolean | No | Yes | Indicates whether the flow runs in debug mode. |
| Flow.StartDateTimeUTC | DateTime | No | Yes | The UTC datetime when the flow started execution. |
| Flow.Version | String | No | Yes | The version of the active flow. |
| System.Conversation | Enum | No | Yes | Information about the conversation associated with the flow. A list of available conversation types. For more information, see mediatype in Conversation Data model in the Genesys Cloud Developer Center. |
| System.MaxInt | Integer | No | Yes | Holds the maximum value allowed for an Integer, which is 999999999999999. |
| System.MaxDateTime | DateTime | No | Yes | Holds the maximum value allowed for a Date Time, which is December 31, 2200 at 11:59:59 p.m. |
| System.MaxDuration | Duration | No | Yes | Holds the maximum value allowed for a Duration, which is 999999999999999 milliseconds (11574074 days, 1 hour, 46 minutes, and 39.999 seconds). |
| System.MinInt | Integer | No | Yes | Holds the minimum value allowed for an Integer, which is -999999999999999. |
| System.MinDateTime | DateTime | No | Yes | Holds the minimum value allowed for a Date Time, which is January 1, 1800 at 12:00:00AM. |
| System.MinDuration | Duration | No | Yes | Holds the minimum value allowed for a Duration, which is -999999999999999 milliseconds (-11574074 days, -1 hour, -46 minutes, and -39.999 seconds). |
| Workitem.Language | String | No | Yes | The lower case IETF language tag for the language in which the flow is currently running. If there is no current flow language, this returns a NOT_SET String. |
| Workitem.Workitem |
Workitem | No | No | The workitem associated with this flow. |
| Workitem.Workitem.assignee | Workitem | No | No | The assignee of the workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.assignee.id | Workitem | No | No | The user ID. |
| Workitem.Workitem.assignee.name |
Workitem | No | No | The user name property. |
| Workitem.Workitem.assignee.username |
Workitem | No | No | The user username property. |
| Workitem.Workitem.assignmentState |
Workitem | No | Yes | The assignment state of the workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.autoStatusTransition | Workitem | No | Yes | This returns true if auto status transition is enabled for the workitem, otherwise false. |
| Workitem.Workitem.customFields |
Workitem | Yes | No | The custom fields defined in the schema referenced by the worktype of the workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.dateAssignmentStateChanged |
Workitem | No | Yes | The date the assignment state changed for the workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.dateClosed |
Workitem | No | Yes | The date the workitem was closed. |
| Workitem.Workitem.dateCreated |
Workitem | No | Yes | The creation date of the workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.dateDue |
Workitem | No | No | The due date of the workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.dateExpires | Workitem | No | No | The expiry date of the workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.dateModified | Workitem | No | Yes | The date the workitem was last modified. |
| Workitem.Workitem.dateStatusChanged |
Workitem | No | Yes | The date the status was last changed. |
| Workitem.Workitem.description |
Workitem | No | No | The description of the workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.divisionId |
Workitem | No | Yes | The division ID which identifies the division to which this workitem belongs. |
| Workitem.Workitem.duration | Workitem | No | Yes | The estimated duration to complete the workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact |
Workitem | No | No | The External Contact associated with this workitem. If there is no External Contact, the value will be NOT_SET. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.address | Workitem | No | No | The address of the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.cellPhone |
Workitem | No | No | The cell phone number of the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.createDateTimeUtc |
Workitem | No | No | The Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) datetime for when the contact entry was created. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.divisionId |
Workitem | No | No | The identifier of the division to which the external contact belongs. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.externalOrganization |
Workitem | No | No | The organization for this contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.externalSystemUrl |
Workitem | No | No | The external system URL of the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.facebookInfo |
Workitem | No | No | The Facebook messaging system user information for the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.firstName | Workitem | No | No | The first name of the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.homePhone | Workitem | No | No | The home phone number of the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.id |
Workitem | No | No | A unique ID for the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.kind |
Workitem | No | No | The internal classification for the record type. For external contacts, the kind will be "contact". |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.lastName |
Workitem | No | No | The last name of the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.lineInfo | Workitem | No | No | The LINE messaging system user information for the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.middleName |
Workitem | No | No | The middle name of the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.modifyDateTimeUtc |
Workitem | No | No | The Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) datetime for when the contact entry was last updated. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.otherEmail |
Workitem | No | No | The other email address of the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.otherPhone |
Workitem | No | No | The other phone number of the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.personalEmail |
Workitem | No | No | The personal email address of the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.salutation |
Workitem | No | No | The salutation suggested when addressing the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.surveyOptOut |
Workitem | No | No | True if this contact has opted out of survey invites. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.title |
Workitem | No | No | The title of the contact. The values are unrestricted, but often values such as "Vice President", "Director", "Employee" are used. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.twitterInfo |
Workitem | No | No | The Twitter messaging system user information for the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.whatsAppInfo |
Workitem | No | No | The WhatsApp messaging system user information for the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.workEmail |
Workitem | No | No | The work email address of the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalContact.workPhone |
Workitem | No | No | The work phone number of the contact. |
| Workitem.Workitem.externalTag |
Workitem | No | No | The external tag associated with this workitem. If there is no external tag, the value will be NOT_SET. Use the Set External Tag action to modify. |
| Workitem.Workitem.id |
Workitem | No | Yes | The workitem ID which uniquely identifies a workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.languageSkill |
Workitem | No | No | The Language Skill associated with the workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.languageSkill.id |
Workitem | No | No | The language skill ID. |
| Workitem.Workitem.languageSkill.name |
Workitem | No | No | The language skill name. |
| Workitem.Workitem.modifiedBy |
Workitem | No | Yes | The ID of the entity that last modified the workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.name |
Workitem | No | No | The name of the workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.priority |
Workitem | No | No | The priority of the workitem. Use the Set Priority action to modify. |
| Workitem.Workitem.queue |
Workitem | No | No | The workitem's queue. |
| Workitem.Workitem.queue.id |
Workitem | No | No | The queue ID. |
| Workitem.Workitem.queue.name |
Workitem | No | No | The queue name. |
| Workitem.Workitem.reporter |
Workitem | No | Yes | The workitem's reporter. |
| Workitem.Workitem.reporter.id |
Workitem | No | Yes | The user ID. |
| Workitem.Workitem.reporter.name |
Workitem | No | Yes | The user name property. |
| Workitem.Workitem.reporter.username |
Workitem | No | Yes | The user username property. |
| Workitem.Workitem.scoredAgents |
Workitem | No | No | A list of agent score pairs used for the last preferred agent routing. |
| Workitem.Workitem.skills |
Workitem | Yes | No | The ACD Skills associated with the workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.status |
Workitem | No | No | The status of the workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.status.category |
Workitem | No | No | The category of the worktype status. Allowable values are "Open", "InProgress", "Waiting" and "Closed". |
| Workitem.Workitem.status.id |
Workitem | No | No | The ID of the worktype status. |
| Workitem.Workitem.status.name |
Workitem | No | No | The name of the worktype status. |
| Workitem.Workitem.ttlDateTime |
Workitem | No | No | The time to live of the workitem until it is deleted from Genesys Cloud represented as a DateTime in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). |
| Workitem.Workitem.typeId |
Workitem | No | Yes | The ID of the worktype for the workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.utilizationLabel |
Workitem | No | No | The utilization label for the workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.utilizationLabel.id |
Workitem | No | No | The utilization label identifier. |
| Workitem.Workitem.utilizationLabel.name |
Workitem | No | No | The utilization label description. |
| Workitem.Workitem.version |
Workitem | No | Yes | The version of the workitem. Note that this may be a NOT_SET Integer. |
| Workitem.Workitem.workbin |
Workitem | No | Yes | The workbin that contains the workitem. |
| Workitem.Workitem.workbin.divisionId |
Workitem | No | Yes | The division ID which identifies the division of this workbin. |
| Workitem.Workitem.workbin.id |
Workitem | No | Yes | The ID of the workbin. |
| Workitem.Workitem.workbin.name |
Workitem | No | Yes | The name of the workbin. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.assignee | Workitem | No | No | The assignee of the workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.assignee.id | Workitem | No | No | The user ID. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.assignee.name |
Workitem | No | No | The user name property. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.assignee.username |
Workitem | No | No | The user username property. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.assignmentState |
Workitem | No | Yes | The assignment state of the workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.autoStatusTransition | Workitem | No | Yes | This returns true if auto status transition is enabled for the workitem, otherwise false. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.customFields |
Workitem | Yes | No | The custom fields defined in the schema referenced by the worktype of the workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.dateAssignmentStateChanged |
Workitem | No | Yes | The date the assignment state changed for the workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.dateClosed |
Workitem | No | Yes | The date the workitem was closed. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.dateCreated |
Workitem | No | Yes | The creation date of the workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.dateDue |
Workitem | No | No | The due date of the workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.dateExpires | Workitem | No | No | The expiry date of the workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.dateModified | Workitem | No | Yes | The date the workitem was last modified. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.dateStatusChanged |
Workitem | No | Yes | The date the status was last changed. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.description |
Workitem | No | No | The description of the workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.divisionId |
Workitem | No | Yes | The division ID which identifies the division to which this workitem belongs. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.duration | Workitem | No | Yes | The estimated duration to complete the workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact |
Workitem | No | No | The External Contact associated with this workitem. If there is no External Contact, the value will be NOT_SET. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.address | Workitem | No | No | The address of the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.cellPhone |
Workitem | No | No | The cell phone number of the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.createDateTimeUtc |
Workitem | No | No | The Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) datetime for when the contact entry was created. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.divisionId |
Workitem | No | No | The identifier of the division to which the external contact belongs. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.externalOrganization |
Workitem | No | No | The organization for this contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.externalSystemUrl |
Workitem | No | No | The external system URL of the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.facebookInfo |
Workitem | No | No | The Facebook messaging system user information for the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.firstName | Workitem | No | No | The first name of the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.homePhone | Workitem | No | No | The home phone number of the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.id |
Workitem | No | No | A unique ID for the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.kind |
Workitem | No | No | The internal classification for the record type. For external contacts, the kind will be "contact". |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.lastName |
Workitem | No | No | The last name of the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.lineInfo | Workitem | No | No | The LINE messaging system user information for the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.middleName |
Workitem | No | No | The middle name of the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.modifyDateTimeUtc |
Workitem | No | No | The Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) datetime for when the contact entry was last updated. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.otherEmail |
Workitem | No | No | The other email address of the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.otherPhone |
Workitem | No | No | The other phone number of the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.personalEmail |
Workitem | No | No | The personal email address of the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.salutation |
Workitem | No | No | The salutation suggested when addressing the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.surveyOptOut |
Workitem | No | No | True if this contact has opted out of survey invites. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.title |
Workitem | No | No | The title of the contact. The values are unrestricted, but often values such as "Vice President", "Director", "Employee" are used. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.twitterInfo |
Workitem | No | No | The Twitter messaging system user information for the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.whatsAppInfo |
Workitem | No | No | The WhatsApp messaging system user information for the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.workEmail |
Workitem | No | No | The work email address of the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalContact.workPhone |
Workitem | No | No | The work phone number of the contact. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.externalTag |
Workitem | No | No | The external tag associated with this workitem. If there is no external tag, the value will be NOT_SET. Use the Set External Tag action to modify. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.id |
Workitem | No | Yes | The workitem ID which uniquely identifies a workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.languageSkill |
Workitem | No | No | The Language Skill associated with the workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.languageSkill.id |
Workitem | No | No | The language skill ID. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.languageSkill.name |
Workitem | No | No | The language skill name. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.modifiedBy |
Workitem | No | Yes | The ID of the entity that last modified the workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.name |
Workitem | No | No | The name of the workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.priority |
Workitem | No | No | The priority of the workitem. Use the Set Priority action to modify. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.queue |
Workitem | No | No | The workitem's queue. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.queue.id |
Workitem | No | No | The queue ID. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.queue.name |
Workitem | No | No | The queue name. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.reporter |
Workitem | No | Yes | The workitem's reporter. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.reporter.id |
Workitem | No | Yes | The user ID. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.reporter.name |
Workitem | No | Yes | The user name property. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.reporter.username |
Workitem | No | Yes | The user username property. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.scoredAgents |
Workitem | No | No | A list of agent score pairs used for the last preferred agent routing. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.skills |
Workitem | Yes | No | The ACD Skills associated with the workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.status |
Workitem | No | No | The status of the workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.status.category |
Workitem | No | No | The category of the worktype status. Allowable values are "Open", "InProgress", "Waiting" and "Closed". |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.status.id |
Workitem | No | No | The ID of the worktype status. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.status.name |
Workitem | No | No | The name of the worktype status. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.ttlDateTime |
Workitem | No | No | The time to live of the workitem until it is deleted from Genesys Cloud represented as a DateTime in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.typeId |
Workitem | No | Yes | The ID of the worktype for the workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.utilizationLabel |
Workitem | No | No | The utilization label for the workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.utilizationLabel.id |
Workitem | No | No | The utilization label identifier. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.utilizationLabel.name |
Workitem | No | No | The utilization label description. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.version |
Workitem | No | Yes | The version of the workitem. Note that this may be a NOT_SET Integer. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.workbin |
Workitem | No | Yes | The workbin that contains the workitem. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.workbin.divisionId |
Workitem | No | Yes | The division ID which identifies the division of this workbin. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.workbin.id |
Workitem | No | Yes | The ID of the workbin. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal.workbin.name |
Workitem | No | Yes | The name of the workbin. |
| Workitem.WorkitemOriginal |
Workitem | No | Yes | The workitem as it existed prior to the event that caused this flow instance to run. |
| Workitem.EventData | Workitem | No | Yes | Holds additional event data for the event that started this workitem flow instance. When a workitem flow instance is started, this variable provides access to data associated with the event that a flow can then use during its execution to get more information about the event. |
| Workitem.EventType |
Workitem | No | Yes | The workitem event type that started this flow. Valid values for event types can be found in Workitem Flow settings. If an event was not responsible for the flow instance, this will return a NOT_SET String. |
| Workitem.Language |
Workitem | No | Yes | The lower case IETF language tag for the language in which the flow is currently running. If there is no current flow language, this returns a NOT_SET String. |
Available Architect actions
This table describes the available Architect actions that you can implement into your workitem flows.
| Icon | Category | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Common | Call Common Module | Reuse previously created logic stored in a common module flow. | |
| Conversation | Set Priority | Set the appropriate priority of the current interaction while it waits in a queue | |
| Set Skills | Set or assign the appropriate ACD and language skills to associate with an interaction while it waits in a queue | ||
| Customer Secured Data | Get Secured Data | Set a secured data attribute that you retrieve from an interaction or workflow participant. | |
| Set Secured Data | Set a secured data attribute value on a call participant. | ||
| Decrypt Data | Decrypt data in Architect flows by using your own encryption key. | ||
| Encrypt Data | Encrypt data in Architect flows by using your own encryption key | ||
| Data | Call Data | Retrieve information about a customer from default or custom data actions integration in Genesys Cloud. | |
| Call Decision Table | Execute a rule-based decision table configured previously by an administrator in Genesys Cloud. | ||
| Data Table Lookup | Retrieve data stored in a Genesys Cloud data table. | ||
| Get Response | Use with the Send Auto Reply action to send an automated reply to a customer. | ||
| Get Conversation Data | Use the Get Conversation Data action in a task to set up an attribute to retrieve from a workflow participant. | ||
| Set Conversation Data | Use the Set Conversation Data action in a task to assign an attribute value on an interaction participant. | ||
| Set External Tag | Associate interactions in Genesys Cloud with records in your organization’s customer relationship management (CRM) system or system of records (SOR). | ||
| Update Data | Assign values to flow or task level variables. | ||
| Update Workitem | Update both built-in and custom attributes of a workitem. | ||
| Disconnect | Disconnect Workitem | Disconnect an agent from a workitem. | |
| Exit Workitem Flow | Exit the workitem flow. | ||
| Terminate Workitem | End a workitem. | ||
| Find | Find Emergency Group | Dynamically find an emergency group based on its name at IVR runtime. For more information, see Emergencies. |
|
| Find Language Skill | Source language skill data from a data dip such as a Call Data action or a data table. Then, use that information with a Transfer to ACD action that sends the interaction to the appropriate queue. | ||
| Find Queue | Find a queue based on its string name at IVR runtime. Use this action to source data from a data action or data lookup tables. | ||
| Find Queue by ID | Reference a queue dynamically and find that queue based on an ID at IVR runtime. | ||
| Find Schedule | Dynamically find a schedule based on its name at IVR runtime. For more information about schedule creation in Genesys Cloud, see Schedules. | ||
| Find Schedule Group | Dynamically find a schedule group based on its name at IVR runtime. For more information, see Schedule Groups. | ||
| Find Skill | Find an ACD skill based on its string name at IVR runtime. Use this action to source skill data from a data dip such as a Call Data action or a data table. Then, use that information with a Transfer to ACD action that sends the interaction to the appropriate queue. | ||
| Find User | Search for a Genesys Cloud user based on an email address at IVR runtime. | ||
| Find User by ID | Reference a user dynamically and find that user based on a string name at IVR runtime. | ||
| Find Users by ID | Reference Genesys Cloud users dynamically and find them based on a string at IVR runtime. | ||
| Find Utilization Label | Dynamically find a utilization label based on its name at IVR runtime. | ||
| External Contacts | Get External Contact | Retrieve information about an existing external contact. | |
| Get External Organization | Use the Get External Organization action to find a specific organization, or with the Get External Contact action to find a specific person. | ||
| Search External Contacts | Find one or more external contacts based on your search terms. | ||
| Flow | Clear Utilization Label | Remove a utilization label from an interaction. | |
| Set Language | Allow callers to select the appropriate language in which to hear prompts. | ||
| Set Utilization Label | Dynamically apply a utilization label to an interaction. | ||
| Logical | Decision | Direct the process branch, depending on whether a condition is true. | |
| Switch | This action is similar to a Decision action, and is easy to set when to evaluate multiple cases. Configure a switch action to specify what Architect does, when to do it, and under which circumstances. | ||
| Evaluate Schedule | Use this action with the Evaluate Schedule Group action to make routing decisions based on previously defined schedules and schedule groups. | ||
| Evaluate Schedule Group | Use this action with the Evaluate Schedule action to make routing decisions based on previously defined schedules and schedule groups. | ||
| Loop | Loop | Direct your process repeat a series of actions before it goes on to the next action in your design. | |
| Next Loop | Use the Next Loop action when, during the loop iteration, the flow encounters a false outcome and you want it to continue to the next iteration. | ||
| Exit Loop | Use this action inside a Loop action. Use it to end and exit the current loop, and to continue flow execution by moving to the following action. | ||
| State | State | Use a state to group tasks together into logical units. | |
| Change State | Jump the process directly to the beginning of a different state without any intervening steps. | ||
| Task | Call Task | Call another task. When the called task completes, the configured output path determines how flow execution continues. | |
| End Task | End a task in a process. | ||
| Transfer | Transfer to ACD | Use the Transfer to ACD action to transfer a caller into a queuing system. | |
| Transfer to User | Transfer a caller directly to a Genesys Cloud user. |