Differences between Journey Management and Journey Flows
Genesys Cloud has two powerful capabilities for customer journey analytics: Journey Flows and Journey Management , which both provide data visualization in Genesys Cloud.
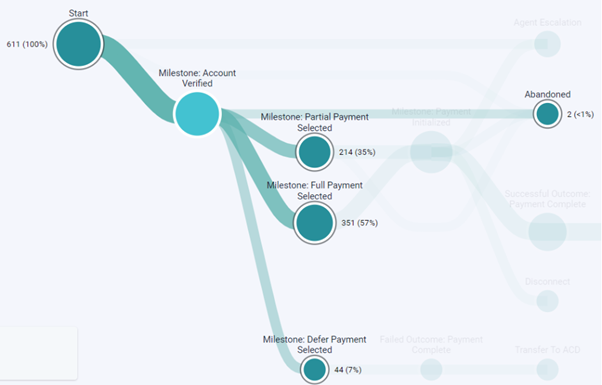
- Journey Flows is an instant view of an individual flow and measures the flow of interactions across branches, milestones, and outcomes of a single journey. For more information, see Journey flows overview.
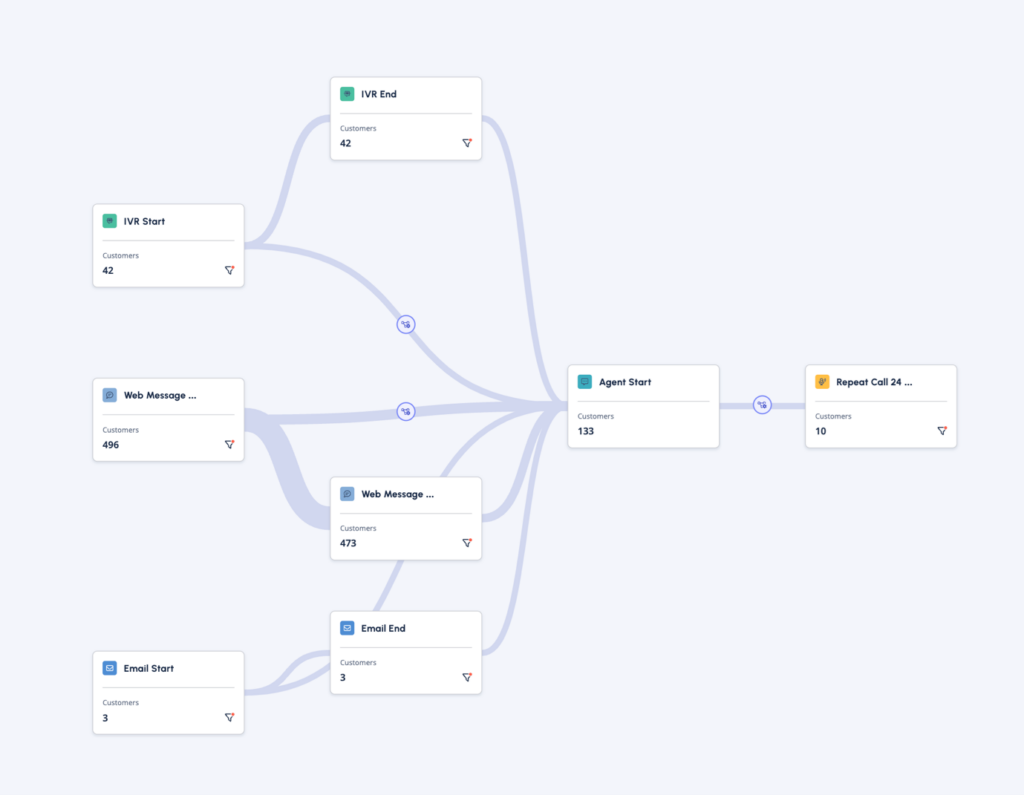
- Journey Management visualizes, measure, monitor and simultaneously optimize CX, EX and business performance by focusing on the journeys your customers take as they seek to achieve a goal. Users can drag and drop events on to the canvas and plot the sequence of events across channels that measure how customers are progressing through a journey. For more information, see About Journey Management.
Key differences
See the main differences between Journey Management and journey flows in the following table.
| Characteristics | Journey flows | Journey Management |
|---|---|---|
| Enablement | Available in Architect. |
Available as a product add-on in any Genesys Cloud license. |
| Data used |
|
|
| Time range | Seven days of data. | Starts with up to 90 days of data and accumulates to a max of 400 days of data to analyze. |
| Configuration |
|
|
| Data update | Updates from the previous night and batch. | Updates from the previous night and batch. |
| Pre- and post-flow activity | Journey flows cannot visualize customer journey data across multiple flows. | Users can create a journey that shows the pre- and post-flow outcome experience; for example, bot to web messenger, voice start to voice bot flow to agent. |
| Use cases | Measure and monitor flow performance step by step and identify points within a flow for optimization. | Users can measure monitor and benchmark first contact resolution, self-service containment, routing efficiency (agent to agent transfers), and improved analyst throughput. Channel behavior Analysis can be assessed in three different ways:
|