Web chat lifecycle
Web chat operation
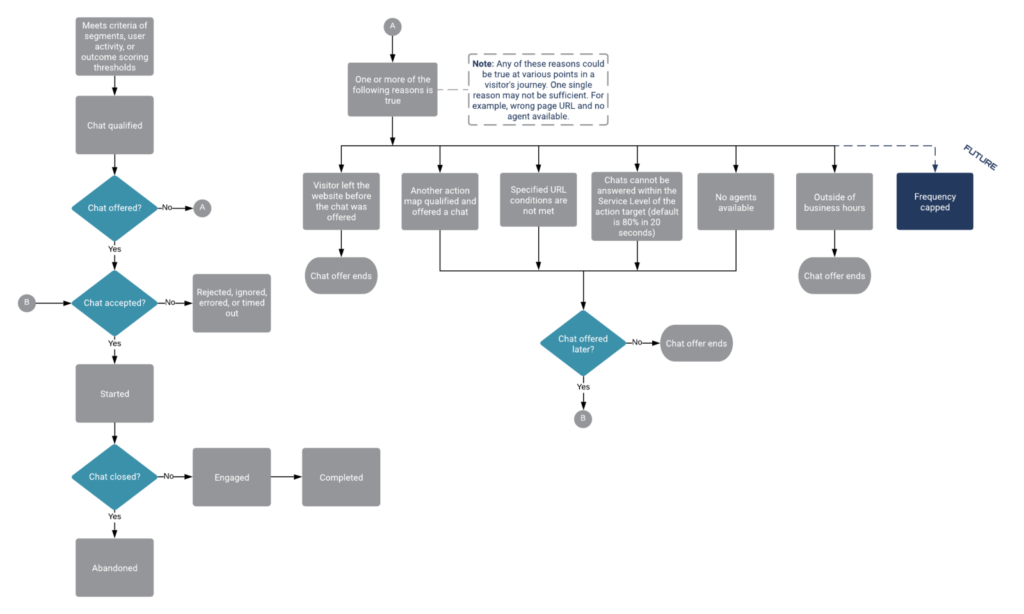
Web chat lifecycle
The following diagram shows the stages that occur during the lifecycle of web chats after offering them to visitors. Subsequent sections provide details about specific states, including the events that can occur and the data that is available for use with the Events methods for web actions. The section, Terminal states, explains how states ensure that visitors do not see the same chat offer repeatedly.
For more information about web chat offering, see Offered action maps.
1. Web chat invitation
| State | Event | Description | Data collected |
|---|---|---|---|
| offered | Web Actions Offered | Visitor’s activity qualifies an action map and triggers a chat invitation. | See Event types for web actions. |
| accepted | Web Actions Accepted | Visitor accepts the chat invitation. | See Event types for web actions. |
| rejected | Web Actions Rejected | Visitor rejects the chat invitation. This state is a terminal state. | See Event types for web actions. |
| ignored | Web Actions Ignored | Visitor ignored the invitation by navigating away from or around it. This state is a terminal state.
Note: This event does not have a corresponding metric in the Action Map Performance Report. |
See Event types for web actions. |
| errored | Web Actions Errored | Error occurred in the widget that prevented the engagement from occurring.
Note: This event does not have a corresponding metric in the Action Map Performance Report. |
See Event types for web actions. Also, the errorMessage field is available. |
| timed out | Web Actions Timed Out | Chat invitation timed out and was rescinded. This state is a terminal state.
Note: This event does not have a corresponding metric in the Action Map Performance Report. The timeout period is configurable through the widget. |
See Event types for web actions. |
2. Web chat form
| State | Event | Description | Data collected |
|---|---|---|---|
| rejected | Web Actions Rejected | Visitor cancels or closes the form. This state is a terminal state. | See Event types for web actions. |
3. Web chat window: before agent connects
| State | Event | Description | Data collected |
|---|---|---|---|
| started | Web Actions Started | After the visitor submits the form, a chat interaction starts. | See Event types for web actions. |
| abandoned | Web Actions Abandoned | Visitor closes the chat window before an agent connects. This state is a terminal state. | See Event types for web actions. |
4. Web chat window: after agent connects
| State | Event | Description | Data collected |
|---|---|---|---|
| engaged | Web Actions Engaged | Agent accepts the chat and connects with the visitor. This state is a terminal state. | See Event types for web actions. |
5. Web chat completion
| Event | Description | Data collected | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Not applicable/Not tracked | Not applicable/Not tracked | Either the visitor or the agent ends the chat.
Note: This event does not have a corresponding metric in the Action Map Performance Report. |
See Event types for web actions. |
Terminal states for web chats
In the web chat lifecycle, certain states are terminal, or final, states. If a visitor visits a web page where an action map is set to trigger a web chat and the web chat is in a terminal state, the action map doesn’t offer the web chat. This action ensures that a visitor does not receive the same chat offer after they accepted the offer or indicated that they are not interested in that chat offer.
Terminal states for web chats are:
- Engaged
- Rejected
- Timed out
- Ignored
- Abandoned
For more information, see Define an action map’s triggers.
Report metrics and events
The metrics in the Action Map Performance report correlate directly with the event types for web actions. For more information about metrics for web chats, see Monitor a web chat’s performance.

