Variables in guides
- Virtual Agent enabled in your organization. For more information, contact your designated Customer Success Manager.
- AI Studio permissions for Guides. For more information about all the required permissions, see AI Studio permissions.
A guide variable enables your AI agent to pass information within the guide. For example, use references between steps in the guide and exchange data with Architect flows during the conversation, making customer’s interaction more dynamic.
Create guide variables
- Click Admin.
- Under AI Studio, click Guides.
- Click Menu > Orchestration > AI Studio > Guides.
- Open an existing guide or create a new one.
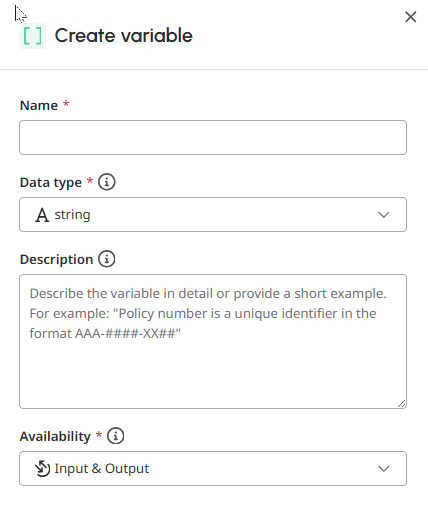
- Open the Variables tab and click Create. The Create variable panel opens.
- Under Create variable, follow these steps:
- In the Name field, enter a variable name.Note: The maximum length of a variable name is 80 characters.
- From the Data type list, select one of the following data types:
- String: A standard text string.
- Boolean: A Boolean can have only one of two values: true or false.
- Number: A number includes any numeric values, including decimals.
- Integer: An integer is a whole number such as 987 or 5. Note: Ensure that the data type matches correctly with the intended values. This behavior improves the large language model (LLM) accuracy when identifying and gathering information.
- In the Description text box, enter a description that is simple and clear. You can also include an example for the data that you intend to store in the variable. For example, A policy number is a unique identifier in the format “XXX-####-YY##”.
- From the Availability list, select the appropriate direction of data transfer.
- Input: Use this direction to send data to the Architect flow.
- Output: Use this direction to receive data from the Architect flow.
- Input & Output: Use this option to send data to or receive data from the Architect flow. Note: For any information used within the guide, the direction can be both or either input or output.
- In the Name field, enter a variable name.
- Click Create. You can now use this variable in your guides.
Variable examples and descriptions
Consider that a variable = variable name + description + data type [+ input/output classification]. The variable must have a meaningful name, a clear description, and an appropriate data type to ensure that the AI agent understands and uses it correctly.
For example, if you want to capture a reservation number, SEQ_1 + 8-digit number + String, may not work as expected. Instead, Reservation_Number + 8-digit reservation number that identifies the booking + numeric, performs better because it gives the AI agent more context about what it must collect.
Ensure that the variable data type matches your business needs.
For example, if you want to capture a reservation code, which could be numeric or string, select the appropriate data type depending on your specifications.
- Numeric – 12345
- String – 1234Oct
If your variable type is set to numeric for something that is string, the guide fails to capture it as the AI agent perceives it as an incorrect information (from the customer).
- Once you have published a guide and connected it to an Architect flow, the variables get locked and you can then update only their descriptions. If you must make significant changes to the variable such as its data type, you must create a new one or duplicate it to edit.
- You can classify your variable as input, output, or both. For any information used within the guide, the direction can be both or either input or output.
- Input: Indicates the information that you want to take in to the guide or use in the guide
- Output: Indicates the information that you want to store or send out of the guide
- If your string variable is a set of specific options, it is recommended that you specify them in the description or the question. If you describe that an option or a value must be from the set list, the AI agent prompts the customer to choose from that list.
- Ensure that you format the dates properly. AI agents are not date aware if you do not tell them the current date. Adjust or phrase the question in a way to capture them correctly.
- Specify the date format that you want in the description, especially if you want to pass that information to a data action.
- Consider that dates and currencies are localized to the runtime language when playing them back to the customer. For example, if the guide is used in Australia, the currency symbols generated by the LLM are converted to AUD$.
A few more examples:
- company_type: The size of the company, for example, one of either small, medium, or large.
- incident_location: The location where the car insurance claim incident occurred in the form of a street address, town, and city.
- branch_location: The location of the branch the customer visited can only be Dublin, Galway, or Cork.
Use variables
- Open an existing guide or create a new one.
- In the Instructions tab, place your cursor where you want to insert a variable and type /.
A pop-up dialog box appears showing options to insert a data action or variable. - Select Variables. The dialog box now lists the available variables.
- Select the required variable. The editor emphasizes variables present in your guide with a gray background.
- Click Save to save the guide or click Publish to publish the guide.Notes:
- While your guide is in draft mode, you can change the guide variables, if needed. After you publish a guide, you cannot change an existing variable’s name, type, or availability, but you can add new variables or edit the description of the existing ones.
- The maximum number of variables that you can have in a single guide is 50.